CEED 2023 Solutions.......very detailed !
Stuff You Look is now in Instagram 😊💥 - stuff_you_look
This page is best viewed from web browser !
1) 8
The situation is shown in the first image below, which represents
the top view of the pentagonal building. A,B,C,D,E represents the watch tower
where the guards are supposed to stand and observe the walls. A guard at
watch-tower 'A' can observe walls 1 and 2. Similarly, a guard standing at say
tower D can watch walls 3 and 4 (adjacent walls) and so on. Considering this
pattern watch guard at each tower can just watch two walls. So, in this case
each wall is being watched by two guards. If you are still not sure of how this
is so continue reading this para or jump to the next para.
- Wall 1 can be watched by person at A and person at B
- Wall 2 can be watched by person at B and person at C
- Wall 5 can be watched by person at A and person at E
- Wall 3 can be watched by person at C and person at D
- Wall 4 can be watched by person at D and person at E
2) 13
For the piece 10 to move to position X, there are many possible ways. Four possible ways are shown as 2(a), 2(b), 2(c), and 2(d). These are the possible shortest paths.
let us try to analyze how many steps are required to move 10 to X as per the path shown in 2[a].
The trick is to start from the empty position (X) and move piece such that the required piece (10) shall be moved towards the position X, as discussed below.
- move 9 to X, which will create empty space (X) at place 9.
- move 5 to previous 9 position (9 is empty due to previous move)
- move 7 to position 5
- Now move 10 to position 7 (which is empty due to previous move step)
This will look like positions as shown in image 2[b] with total 4 steps so far
Now, let us move number 10 to one step ahead, to position 7. For this do the below steps (also shown in figure 2[c]
- move 8 to X
- move 7 to 8
- move 10 to 7
This will create an empty position at position 10 as per fig
2[c], which is shown in fig 2[d]. Total steps so far are 4+3 = 7. Let us now
move number 10 to position 5 by following the steps shown in fig 2[d].
- move 4 to X
- move 5 to 4
- move 10 to 5
This will create an empty position at position 10 as per fig
2[d], which is shown in fig 2[e]. Total steps so far are 7+3 = 10. Let us now
move number 10 to position 9 by following the steps shown in fig 2[e].
- move 12 to X
- move 9 to 12
- move 10 to 9
Total number of steps needed for the entire moves are 10+3 = 13.
3) 16
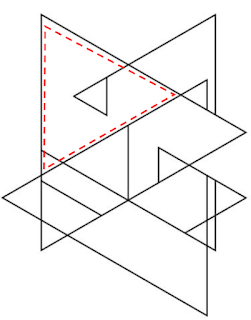
I usually follow the pattern of identifying the number of shapes without any collision and then step by step identifying the other required shapes that are colliding with the other part of the shape. In the first image, I’ve highlighted the triangles that are not colliding with any other part of the image. For similar questions, which needed different method, I would go by either left to right and then top to bottom….to count the shapes. The method that I choose depends on the complexity of the image being given.
4) 3
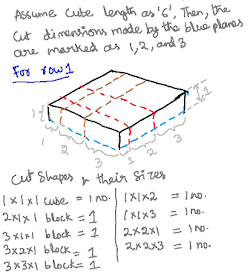
In the first figure I’ve shown the planes (at 1/6th
and 1/2th) as mentioned by the question in three directions. I’ve shown dotted
lines with different colors to indicate the cuts. Assuming the total cube side
as 6, the first cut will be at length 1, second at the mid (length 3) as shown
in the first figure.
Considering row 1 I’ve highlighted the blocks that can be obtained by the cutting planes. I’ve also listed the blocks based on their dimensions. Only one block turned out to be a cube of dimension 1x1x1
Similarly in the second figure, I’ve shown the obtained
blocks for the second row with depth as 2. Only cube is possible with dimension
2X2X2.
In the final figure, again only one figure is possible with
dimension 3X3X3. Note that for explanation I’ve shown all these figures but
during exam I would try to imagine the cuts and identify only the cubes with
all dimensions same. And it is obvious that we can expect only one cube of each
possible dimension (1, 2, and 3)
5) 20
According to the given first condition, Robert can buy
either 50 apples or 40 bananas with his monthly allowance. Let the allowance be
X. Let the price of each apple be ‘a’ and the price of each banana be ‘b’. So,
X = 50*a (or)
X = 40*b
Which mean, (here * means multiply)
50*a = 40*b
40*b = 50*a
b = (50/40)*a
As per the question, one month he decides to save 10% of his
allowance, which mean he is going to spend only 90% of his regular allowance (90/100*X
= 0.9*X). Out of which he already bought 20 bananas.
If he only has to buy Bananas, he could buy 0.9*40 number of
bananas, which is 36 bananas. That’s because the price of the apples or bananas
ae going to be the same and only the quantities are going to reduce due to
reduced budget/allowance. since he bought 20 already, he could only buy 16 bananas
(out of 36 bananas) with the leftover savings
16*b = 16*(50/40)*a = 20*a
Which means he could buy only 20 apples (which his
equivalent to 16 bananas) with the leftover allowance.
6) 42
This is not a difficult question to solve if you understand
something I call ‘surface continuity’ which means the continuation of a surface
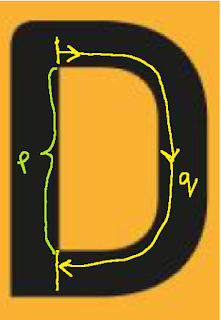
if it is curved. Let us take the first alphabet and explain this.
Considering letter ‘D’, observe the edges (as shown in the
top view) carefully. Even though the alphabet seems to have edges (a,b,c,d,e,
and f) they can actually be treated as continuous. So, I count the outer
surface as 1. In the next figure I’ve mentioned the possible surfaces (p and q).
Again, q is continuous and so it is counted as 1. For Alphabet D, total no. of
surfaces including the first and second figure of D is 1 + 1 + 1 (this is
without counting the top surface)
Similarly, for the other alphabets I’ve marked the surfaces
For E, side surfaces count is 11
For S, side surfaces count is 4
For I, side surfaces count is 3
For G, side surfaces count is 6
For N, side surfaces count is 9
Apart from this, each alphabet in the top will have one surface (D, E, S, I, G, N) total top surface count is 6
Therefore, total surface count = 3+11+4+3+6+9+6 = 42
7) 13
There are total 4*4 = 16 number of Q letters. I will just
identify the repetitions and eliminate those no. from the 16 to make it easy
for me. By observation I’ve highlighted the repetitions (in different color)
for your understanding. Now, I can remove those repetitions to get 16 -3 = 13
Tip: first observe the tail to see similarity/difference. Then you can observe the width of O to see if the fonts are different even if the tails appear to be same.
8) 2
First, we need to find the radius of the rotating pin-disk.
The ide is simple. We need to know the circumference of the small rotating
circular pin-disk and also the circumference of the bigger circle (having
radius 10cm). Then The circumference will help in knowing how many times the
disc has to rotate to complete the circle. If you are not sure, what do I mean
by Circumference, refer my video on ‘basic math for design exams’. Circumference measures the total length of the
circular line and so the idea here is we need to know how many times the total
length of the disc circle coincides with the total length of the big circle as
the disc rotates. These solutions are prepared by Bhanu Chander and copyrights
to Stuff You Look blog. If you see these solutions in any of your coaching
institute material then it shows how degraded your institute is. They should be
ashamed of copying SYL content just to make money.
As shown in the figure, we need to find R first, which is side AC, given side AB and 30 degrees. The calculations are shown in the below figure. We get R=5cm
Circumference of the bottom big circle with radius r=10cm is
2.PI.r = 2*3.14*10 = 62
Circumference of the rotating disc with radius R=5cm is
2.PI.r = 2*3.14*5 = 31
Now, Let us assume the pin-disc needs X turns to complete.
So, X*31 should be greater than 62. Which mean
X*31 > 62
X > 62/31
X > 2
So, the pin-disc should make atleast 2 turns to make a
complete circle on the base circle.
9) A, B, C
Let us assume the two cuts as R for rectangle and T for
triangle as shown in the first figure. The
next two figures explains how I was able to identify the cut shapes.
10) A, B, D
The ide is simple. You need to observe the movement of the
end marked as B with the push at end A as shown in the first image. As show in
the second image, in both the options A and B, when we step/press at A, due to
the mechanisms, they tend to push the knob of the sanitizer as shown by arrows
and hence they can work. In the next image, shown as option C, when we press
the end A, due to the pivot at the bottom the entire mechanism will try to
raise up and hence the sanitizer will not work. In option D, when we press the
knob, and since there is a pivot at P, the mechanism will try to lower at B as
shown by arrows in the third image. Thus, the sanitizer will work.
11) B, C
A is wrong because specific elements are arranged in a
repetitive manner. For ex. 72 beats every minute, 6 degrees every min, structure
consisting of SERIES of beams and nodes.
D is wrong because scales are indicative of time but not
volumes
12) C, D
Before inspecting the options, I wish to explain the basics
so that it will be easy for you to solve similar kind of physics related problems.
Assuming you are trying to sip juice from the bowl as shown
in the first image using a straw. For explanation purpose I’ve shown a thick
straw of higher diameter but practically we will be using a thinner straw
(small dia). As you start sucking air, mentioned as 1 circled in the figure
shown, you have removed the air inside the space of the straw. As you continue
to sip and since there is no air left vaccum will be created inside the straw
with zero pressure, marked as 2 in the figure. Since the pressure at this
specific location is lower than the outside pressure, the atmospheric pressure
shall try to push the liquid down and acts all along the surface area of the
liquid that is exposed to the atmosphere. This is shown as 3 in the same
figure. This higher pressure (compared to zero pressure in the straw) will make
the liquid in the straw raise, making it reach to the end of the straw and
hence you will be able to sip the juice.
In option A and B, since the junction J is above the surface (AB) of the liquid no matter how much try to sip by sucking air the liquid will not raise. This is because air from the side straw will be sucked as shown in the figure 2. In options C and D, the junction J is below the surface of the liquid and hence whenever we sip through the straw the juice will be sucked as the straw is not connected to the secondary straw through which air can be taken like in option A and B. Note that in option C, the liquid will be sucked only till the liquid level falls in line with J. After that the side straw gets connection to the main straw and hence air will start sucked from the side straw, making the juice undisturbed.
13) A, B, C
I don’t think I’ve to give explanation for this question as
it is straight forward (the rotation thing). Anyways, here are a few tips for
you to solve this question.
135 degrees anti-clockwise is same as 45 degrees (180-45)
clockwise given that the given pattern is symmetry and replicates the same
pattern if we rotate it 180 degrees.
90 degrees clockwise is same as 90 degrees anti clockwise
and after 90 degrees clockwise or anticlockwise, the patterns coincides and so
it will look the same in top view (check option C)
14) A, B, C, D
All the stake holders
are required to be asked for feedback but the order of importance should start
from the user and the end user should be given the highest priority whenever we
make designs or products. If you ask me, I will give the following order of
importance (I might be wrong, but I strongly feel the below order based on my
experience)
- Existing user,
- customer support,
- People who deliver food,
- Employees who offer food
15) A, B, D
I’ve shown in the figure how I’ve arrived at the required
image for the possible options. Follow the numbers 1,2,3 for the correct order
of obtaining the completed image
16) B
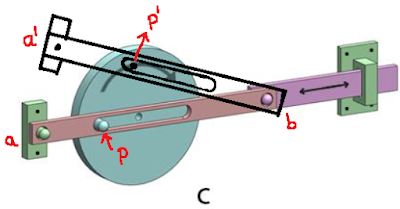
Let us mark the pin as P as shown in the first figure. Even
if we rotate the disk as indicated by the red arrow, the whole arm might tend
to angle but this will not affect the position of the purple metal bar.
In option B, if we turn the disc such that Pin T is now T’ after the slight rotation, the position of the connecting slider, denoted as PQ will be P’Q’. This mean the entire purple metal slider will be able to move. Let’s say we mark points R and S before the rotation, they will be at R’ and S’ respectively after the rotation. This mean the bar is making a linear motion.
Option C is somewhat similar to option A, where even after the disc rotates to some degrees as shown in figure (from a-b to a’-b) only the connecting rod in brown color will turn while the connecting end at b will mostly stay at the same position.
In option D, the contacting point at P will remain at the same location (P’) even if we rotate the disc (say point a moves to a’)and this will not at all affect the position of the point P or P’ on the purple colored metal slider. This mechanism will not work.
17) B, C
A is not possible because the curve should be deep. In the following figures. I've drawn and shown how the cam (non-cylindrical) rear wheel is causing extra projection/curvature. Note that due to the shape of the rear cam/wheel, the curve traced by the pencil is deep.
18) A, D
I think the answers are straight forward because it is a
simple rotation inspection question. Still, I will try to give a quick hint on
how to identify the correct options. I’ve marked the directions (which I
usually follow). Option A is the rotation view of the given image. Visualize
the backside view of option A and flip it horizontally (upside down) and you
will be able to see the front view of the given object.
Backside view of option D is the front view of the given object. (These whole solutions are the work of Bhanu Chander of Stuff You Look. If you chanced to see these solutions in any other platform like in your coaching institute’s study materials then they have simply copied from SYL blog. Now you know how genuine they are). In the next two figures I’ve given explanations of why they are not the rotated views.
19) D
I think most of you would’ve answered this already. Regardless
I will share my thoughts on this. When operating with right hand it is easy to
reach the lower right portion of the keypad. Orange is the first easiest to
reach, followed by green. However, since it is a small key we consider red as
the next easiest key to press followed by green. Blue is the least easy key to operate
with right hand.
20) D
I would solve this question by looking at the lengths ‘x’ and
‘y’ as shown in the figure. The length x is slightly greater than or equal to the
length y. Considering this requirement option A and B are definitely not the
correct ones. Out of option C and D, I would look for the correct pattern of ‘p’
and ‘q’ portion as shown in the second figure. In option C, location p has a solid
instead of empty. Hence D is the correct option.
21) A
Teak is a hard wood. It is strong and durable, able to
withstand extremes of heat and cold. It is very versatile material. It has many
applications including building construction work, interior and exterior
furniture, doors and window frames, flooring, deck decks and the like. An
outstanding feature of teak outdoor furniture is the ability to withstand all
types of weather. It is one of the few woods in the world containing a natural
oil which repels water, keeping it from warping, cracking or becoming brittle.
Teak wood can be carved by hand to create more intricate furniture.
Hardwood plywood is a great choice for furniture, cabinets,
and many other projects due to its strength, stability, and convenience.
Plywood is High impact resistance, High strength to weight ratio, Environmentally
Friendly, Durable, and Cheaper than Solid wood. Not always easy to sculpt on
this. Without some special resistance method maximum after long-term get
attacked by insects.
MDF is a softer material than plywood and tends to sag or
split under pressure. MDF doesn't handle moisture very well, either, so it is
more suited for indoor use, such as in furniture. is generally cheaper than
plywood. MDF board would be the best option if you want a low budget and
material for interior application. If you want material for an exterior
application that can withstand moisture, then plywood is the best option.
Particle board is cheaper, denser and more uniform than
conventional wood and plywood and is substituted for them when cost is more
important than strength and appearance. IParticle board is cheaper, denser and
more uniform than conventional wood and plywood and is substituted for them
when cost is more important than strength and appearance. Not ideal for
heavy-duty use. The disadvantages of particle board include its susceptibility
to damage, lack of water-resistance, and its incompatibility with drilling (so,
cannot handle screws)
22) A
Since the zoo keeper got the information that 7 animals have
escaped and out of that he deduced that atleast one baboon would’ve escaped –
it would mean that the number of monkeys would be definitely less than 7. Only
then it is possible for him to assume that one or more baboons have escaped.
Looking at the options, y should not be more than 6. A is the impossible option
then.
23) C
The Blue Period is a term used to define the works produced
by Spanish painter Pablo Picasso between 1901 and 1904 when he painted
essentially monochromatic paintings in shades of blue and blue-green, only
occasionally warmed by other colors. Below image taken from Wikipedia is one
example of Pablo’s ‘The Old Guitarist’ painted during the blue period, the
period when he was in depression and was using mostly blue and blue-green
shades.
For a detailed study on types of color themes refer the
below two websites:
Color Theory 101: A Complete Guide to Color Wheels &
Color Schemes -
24) A
As shown in the
figure, face ‘a’ will be turned when we try to unwrap it. So, whatever the printing
(top part of ‘Marker’) will not appear in the unwrapped front portion of the
paper format shown in the options. And in
the unwrapped view of the page the ‘b’ portion will be the first to be visible
from the top as marked in the figure. Based on this, only option A is seen to
fit.
25) C
I feel task 2 and 3 should be on the same height while
washing utensil shall be on a different height (usually lower height)
26) C
First, I will try to see if by using the given options, will
I be able to draw a vertical line, which is required to complete the fish, and
if yes, then will the tracing and replication be possible between blue and red?
The triangular link as highlighted in the figure for option A
will make it difficult for the mechanism to achieve the goal. In option B, if x
and y are of same length then there is a possibility for the fish to be traced.
But the traced fish would be of the same size.
Option C is a very famous mechanism and the beauty of it is that it can help in drawing straight lines (esp. vertical line) using the ends (blue and red ends). Option D is uncontrollable and even if we move blue end most of the times red end won’t respond and there is not proper connection between the two links. This is not a good mechanism. A good mechanism should enable you to control the movement of an end as per your needs and as you expected.
27) C
We want to find the pattern after one and half hour, which
mean after 90 mins. Given
In every 15 mins dial Q rotates by 90 deg clockwise, and
after every 30 mins dial P rotates by 45 deg anti-clockwise
In 90 mins,
(Since 90 mins = 6 times 15 mins) Dial Q rotates by 6 times 90
degrees (540 degrees) clockwise. This 540 degree can be taken as one complete turn/circle
(360 degrees) and 540-360 = 180 degrees turn, the shape of which is as shown in
option A.
In 90 mins,
(Since 90 mins = 3 times 30 mins) Dial P rotates by 3 times 45
degrees (145 degrees) anti-clockwise. Which mean 45 degrees clockwise. If we
rotate P by 45 deg clockwise it will look like the shown figure. Now, if we
overlay the rotated view of Q (which is shown in option A) on top of the
rotated Q shape as shown in the below figure we should be able to see option C.
28) C
First of all, stacking mean placing chair on top of chair
when the chairs are not in use. Stacking is possible only when the width of the
supports (shown as ‘x’ in the figure) is higher than the width of the seat (shown
as ‘y’ in the figure). In all the options the width ‘x’ is either same or
higher than ‘y’ and hence stacking will be difficult. This is in mathematical terms,
so let me put it in simple language. The backward legs should be slightly
protruding out of the seat, only then we can make another chairs seat to stack
(else there will be no space to make it sit due to the chair legs interruptions).
I hope you are able to visualize and understand.
29) B
Egg and sugar and two separate elements and will go into
making cake. Option A suits this where the two small hexagons are representing
egg and sugar individually and the larger hexagon represent the cake, which
holds the two elements.
Because of seed came tree and because of tree came fruit.
And this is represented by option D (small shape inside a medium sized shape
and medium inside a big shape)
Rock, paper, and scissors are three contrasting objects and
hence option C suits, as the three shapes are shown no relation between them.
Option B is weird as the two small shapes are shown
intersection (union) which is not indicated by any of the three given relationships.
30) A
Looking at the options I feel the circles meant the owner of
the dog (the sisters) and the triangles represent their dogs and the scribbling
represent the movement of the dog and their distance. Considering this
hypothesis, as per the given instruction, the elder sister (bigger circle)
should be at the center while her dog (a triangle) should lie near to the
bigger circle. The middle sister (the medium size circle) should lie inside the
fence along with its dog, and the younger sister should be outside the fence
with its dog little far from her as compared to the distance of the scribbling
of the middle sister (given that her dog is running and chasing squirrels)
31)
I’m kind of lost in understanding what is happening with
this question. But I tried my best to list about the details of the info that
these paintings carry. Below set of figures should give you some info.
32) C
Scissors shown in option D is not meant for breaking nuts. A
is the worst design as the pressure applied to the nut is very minimal given
that the handle are very close to each other. The more the distance of the grip
end from the pin p (shown as x) and the more the end-to-end distance (shown as
y in the figure) for the user to hold the better will be the cutting pressure. Plier
shown as option C provide greater pressure, followed by option B.
33) B
What I know is when a camel gets up from its seating
position it generally uses its right front leg first before using the right
left leg along with the hind legs. Keeping this in mind I could see only option
B where from 1 to 2 the direction of movement is towards left. From 4 to 8 it
rightly indicates the movement from left to right.
34) C
Considering green circle with no straight sides as 0, triangle
with three sides as 3, rectangle with four sides as 4, pentagon with five sides
as 5, and finally six side hexagon as 6.
Now, sum the number of sides in every row or even column.
Like in first row, we have
1 hexagon + 2 rectangles + 1 circle = 1*6+2*4+0 = 14
Consider the third row
3 triangles + 1 pentagon = 3*3 + 5 = 14
Similarly, you can check for last row as well. It will sump
up to 14. Considering this if we sum up the 2nd row it should be 14.
1 pentagon + 1 rectangle + 1 circle + ? = 5+4+0 + ? = 9 + ?
So the ? should have 5 sides in order for it to sum to 14
35) B
Observe the distance x and y in first figure. Also, the top
surface ‘ts’ is flat while the bottom surface ‘bs’ is cut slant. In options A
and C, the top surface ‘ts’ are not straight and hence they are incorrect. Now,
inspect the distance ‘y’ in options B and D. Option B seems to fit as y should
be short unlike in option D.
36) C
The best way to solve these kinds of unfolding problems is
to move in reverse on how it got folded. This I’ve shown in the figure.
37) C
This is pretty straight forward.
38) B
By observation
39) A
As shown in the figure, because of the curved surface, the
reflection would look like this. It will appear upside down due to the light
rays from the object.
40) C
By observation I tried to match the mirror image of the
given pattern and C turned out to be the perfect match. As shown in the figure
I’ve highlighted the patterns that I considered as a deciding factor, ordered by
the numbers shown. These solutions are the copy right of stuff you look blog.
41) A
As shown in the below figure, I’ve highlighted the portion
of the patterns that distinguishes between the correct pattern and the wrong
pattern. Highlight ‘P’ is the deciding factor in eliminating options B and D,
and highlight ‘Q’ is the deciding factor in eliminating the C option.
 |
I hope my solutions have helped you to a good extent. Support Stuff-You-Look blog by ignoring the scam-sters who try to steal this blog's content and the solutions shared. Follow SYL in FB and Insta to keep yourself updated of the latest releases. All the very best with your start!





















































This comment has been removed by the author.
ReplyDeleteHi Bhanu
ReplyDeleteI'm the creator of Prepzilla, a free, non-commercial platform offering CEED PYQs with analytics.I've seen your detailed CEED solutions on Stuff You Look and consider it one of the best open source and credible learning resources in this space.
I'm writing to request permission to reference/republish your CEED answer explanations (with full credit and linkbacks to your site) within Prepzilla. The goal is to make preparation easier for aspirations while ensuring your authorship and blog visibility remain intact.
If you'd prefer, I can embed excerpts and direct users to your full posts instead of mirroring them (but this will hurt the UX).
Would you be open to discussing how we can collaborate or attribute your work appropriately?
There are currently 120 active users on the platform and I am listening to their feedback and building features that help them with Part A.
Thanks for your time and for sharing such valuable explanations publicly.
Best
Ritik
nice
ReplyDelete